Understanding Surgical Tools: Essentials for Modern Medicine
Surgical tools play a critical role in healthcare, ensuring that doctors can perform procedures with precision and efficiency. From simple instruments to advanced robotic systems, the evolution of these tools signifies the advances in medical technology and the relentless pursuit of improving patient outcomes. This article dives deep into the world of surgical tools, examining their types, uses, maintenance, and their indispensable role in modern healthcare.
The Importance of Surgical Tools in Medical Practice
In the medical field, the effectiveness of surgical procedures largely depends on the quality and functionality of the surgical tools utilized. These instruments are designed for various tasks, including:
- Dissecting: Cutting and separating tissues.
- Clamping: Holding tissue or organs in place.
- Suturing: Closing incisions or wounds.
- Monitoring: Keeping track of vital signs during procedures.
Each surgical tool is engineered to fulfill specific operational requirements, which is why understanding their uses is fundamental for healthcare professionals.
Types of Surgical Tools
Surgical tools can be categorized based on their function and design. Here are the primary categories:
1. Cutting Instruments
These instruments are primarily used for cutting tissue. Common types include:
- Scalpels: Utilize a thin blade for precise incisions.
- Scissors: Designed specifically for surgical use, allowing for smooth and accurate cutting.
2. Grasping and Holding Tools
These tools are essential for holding tissues in place during procedures. Examples include:
- Tissue Forceps: Used to grip and manipulate tissue safely.
- Hemostatic Forceps: Designed to clamp blood vessels to control bleeding.
3. Retractors
Retractors are crucial for holding back organs and tissues to provide the surgeon with a clear view of the surgical area. They come in two types:
- Handheld Retractors: Require manual operation to hold back tissue.
- Self-Retaining Retractors: Mechanically hold tissue in place, allowing surgeons to operate with both hands.
4. Suturing Instruments
Suturing is a vital part of many surgical procedures. Instruments used for suturing include:
- Suture Needles: Used to stitch tissues together.
- Suture Scissors: Designed specifically for cutting sutures after closure.
Technological Advancements in Surgical Tools
The field of surgery has witnessed rapid technological advancements that have transformed the landscape of surgical tools. Notable innovations include:
1. Minimally Invasive Surgical Tools
Minimally invasive procedures require specialized tools that allow surgeons to operate through small incisions. These tools often include:
- Laparoscopes: Equipped with cameras to provide visual feedback.
- Endoscopes: Allow examination and treatment of the gastrointestinal tract without large incisions.
2. Robotic Surgical Systems
Robotic surgery represents a groundbreaking advancement, offering unprecedented precision. Notable systems include:
- da Vinci Surgical System: Enhances dexterity and precision of the surgeon’s movements.
- MAKO System: Utilizes robotic assistance in orthopedic surgeries, increasing accuracy.
3. 3D Printing of Surgical Tools
3D printing technology enables the production of customized surgical instruments tailored to individual patient needs. The benefits include:
- Customization: Instruments can be tailor-made for specific surgeries.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Reduced waste and lower production costs compared to traditional manufacturing.
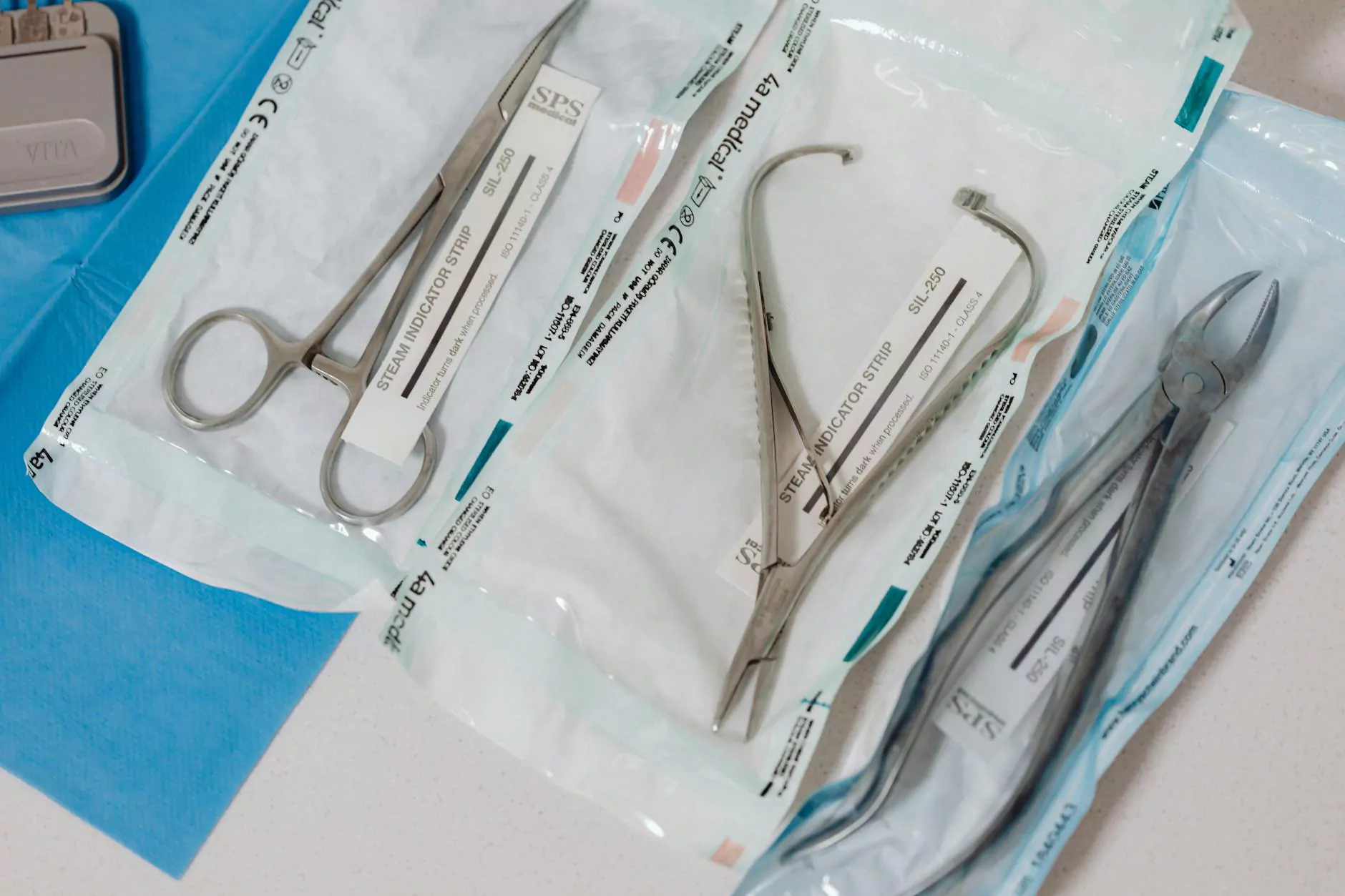
Maintenance and Sterilization of Surgical Tools
Proper maintenance and sterilization of surgical tools are essential for patient safety. The following practices should be adhered to:
1. Cleaning
Instruments must be thoroughly cleaned after use to remove blood, tissue, and other contaminants. This involves:
- Immediate rinsing to prevent drying of blood on surfaces.
- Utilizing ultrasonic cleaners for effective deep cleaning.
2. Sterilization
Surgical instruments should undergo sterilization before being used on patients. Common methods include:
- Steam Sterilization: Commonly known as autoclaving, utilizes high-pressure steam.
- Ethylene Oxide Sterilization: A gas sterilization process suitable for heat-sensitive tools.
3. Regular Inspection
Inspecting surgical tools for damage or wear is crucial. Any instrument that is not functioning correctly can compromise surgical outcomes. Healthcare facilities should implement routine checks and maintenance schedules.
The Role of Surgical Tools in Patient Outcomes
The effectiveness of surgical tools directly influences patient outcomes. The right tool enhances a surgeon's ability to perform complex procedures safely and efficiently, thus improving recovery times and reducing complications. For instance:
1. Reducing Surgical Complications
Quality surgical tools enable precise incisions, less tissue trauma, and reduced bleeding, leading to fewer complications.
2. Faster Recovery Times
Minimally invasive instruments, such as laparoscopic tools, allow for quicker recovery times, enabling patients to return to their daily routines sooner.
Conclusion: The Unseen Heroes of Medicine
The world of surgical tools is complex, yet vital to modern medicine. Understanding the various types, advancements, and proper care of these instruments can significantly impact surgical outcomes and patient care. As technology advances, the future of surgical instruments is bound to further evolve, promising even greater achievements in healthcare.
Final Thoughts
Whether you're a healthcare professional or someone interested in the medical field, familiarizing yourself with surgical tools is essential. Every tool has a purpose, and their significance cannot be overstated. For healthcare providers, ensuring the utmost quality and maintenance of surgical tools is paramount in delivering safe and effective surgical interventions.
Learn More
For more in-depth information about surgical tools and advancements in healthcare, visit grey-medical.com for a wealth of resources and insights.